Blockchains are gaining popularity for their applications in both public and private enterprises. Privately, individuals can use blockchains as a store of wealth that is beyond the control of governments and hackers. Publically, blockchains are being used to design better systems for logistics, finance, and governance. The power is derived from the fact that the data stored on blockchains are resistant to tampering and is transparently available for all of the users to access. However, there remain some applications that are not covered by either public or private blockchains alone. Here’s a look at why hybrid blockchains are required and how they can solve everyday problems.
Hybrid Blockchains lie somewhere between private and public blockchains, depending on their architecture. Therefore, to get a good understanding of hybrid blockchains, one must first understand the differences between private and public blockchains. As the name suggests, public blockchains are accessible to and managed by the public. Anyone can participate in the maintenance and governance of the blockchain. The most popular blockchain in the world, Bitcoin, is a public blockchain. Participators are typically rewarded in the form of block rewards for their contributions to the network to incentivize good behaviour on the part of network peers. Since millions of users manage a public blockchain across the world in real-time, achieving consensus for a public blockchain is time-consuming and expensive. For instance, the consensus mechanism that Bitcoin uses, Proof of Work, relies heavily on wasteful computations for millions of devices to ensure security. By comparison, a private blockchain allows limited access to entities outside a trusted few who were involved in the creation of the private blockchain. Typically, private blockchains have administrators who can control the permissions of adding or modifying data on a private blockchain. The most popular private blockchains include the hyper ledger fabric which is being developed as a competitor to Ethereum by IBM and quorum, which is being developed by J.P. Morgan. Private blockchains are much faster than public blockchains because the network is managed by a handful of trusted nodes whose motives are clearly for the benefit of the network. Such trusted nodes typically belong to financial institutions or universities to maintain fairness and remain unbiased.
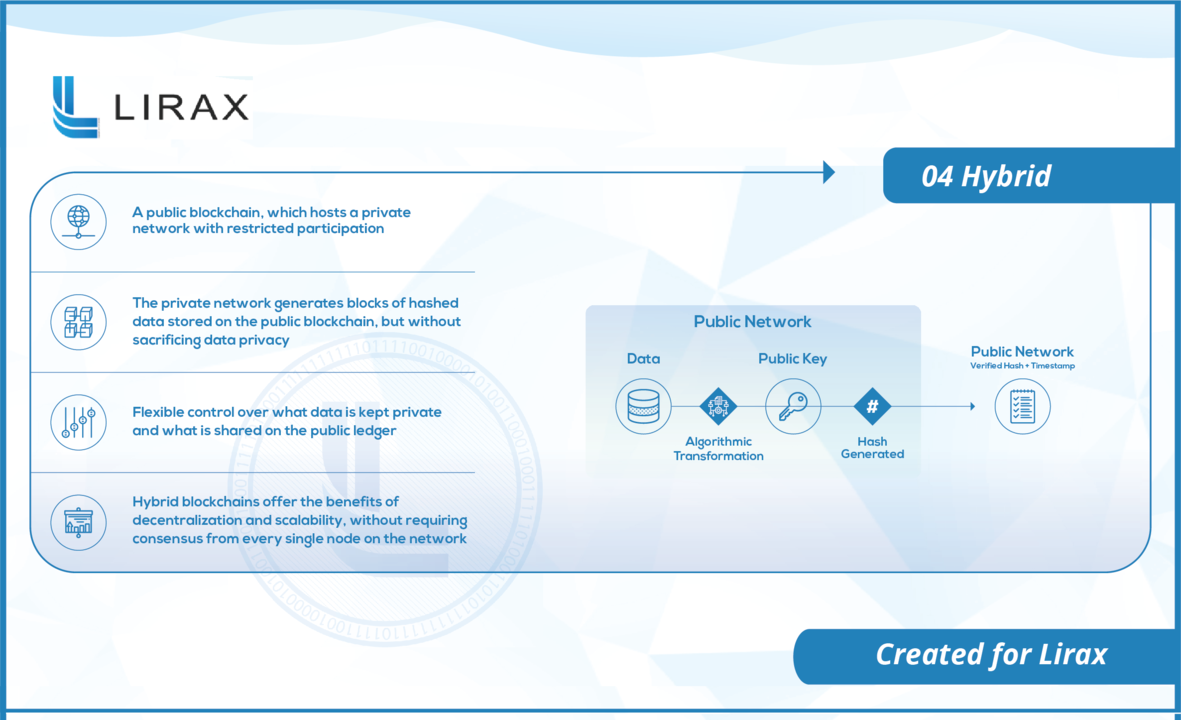
Now, it is clear that each type of blockchain has its strengths and weaknesses. Public blockchains while being transparent and resistant to tampering are slow and expensive whereas, private blockchains are somewhat centralised but can deliver much higher throughput and speeds. As a logical step, hybrid blockchains combine the benefits of both of the blockchains while trying to limit the disadvantages. Therefore, with hybrid blockchains like LIRAX, we can employ a public blockchain to make the ledger accessible to every single person in the world, with a private blockchain running in the background that can control access to the modifications in the ledger.
LIRAX – Hybrid Blockchains
One of the leading hybrid blockchain platforms, LIRAX, has developed a unique network for the management of supply chain jewelry. LIRAX developed its public-private blockchain on Ethereum (public blockchain) and on a private blockchain. There are numerous benefits to using a hybrid blockchain like the speed of private blockchains combined with the security of public blockchains. The private blockchain is used to generate a hash of transactions which is later verified using the public blockchain.
Another real-world application of hybrid blockchains includes the Ripple network and the XRP token. Ripple has regularly been criticised for its centralised nodes which can arbitrate transactions in the case of a dispute. But by adding a public blockchain to verify the operations of its private blockchain can make the network much more secure for its users.
#Blockchain #Hybrid #Lirax #Ripple #LRX #Ethereum #IBM #JPMorgan #Civati