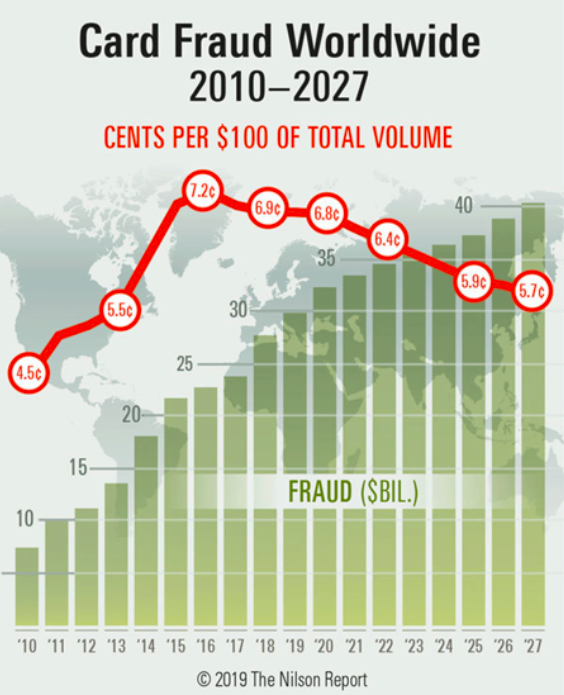
Payment fraud is the most common type of theft, according to a 2020 Federal Trade Commission report. This type of scam typically entails taking over a person’s existing credit card accounts and charging without permission or opening new accounts using someone else’s personal financial information. Let’s understand how to coping up with payment frauds with blockchain (includes credit card thefts).
Worldwide, financial transactions are targeted by fraudsters, and according to IBM, payment fraud is more than $20 billion in issues annually. On the other, CNBC reports that last year’s fraud and identity theft have resulted in a $16 billion loss.
With such massive losses caused to the payment industry regularly, several financial institutions and credit card companies have taken up measures that alert the customer when a fraudulent transaction attempt is made. With this, the system may stop a fraudulent transaction from taking place, but it doesn’t prevent data that gets stolen and used without permission. In most cases, hackers escape with the money, and the customer is left to deal with the credit, financial, and psychological damage.
In a survey conducted by KPMG in 2019, it was discovered that only 57% of enterprises assess fraud risks across the world. Also, only 69% maintained a fraud committee.
We cannot agree more that protecting your debit/credit accounts and personal identity is imperative, and it begins with blockchain technology. With blockchain, all the sensitive data can be stored in the form of “secured, tamper-proof digital records.” The technology offers the possibility of keeping the information in a centralized or decentralized manner.
When a transaction is performed on the blockchain, it is possible to keep track of the wire transfer sequence. As the distributed ledger technology promises transparent and trusted transactions, it is one of the most sought after technology being explored by the banks and other financial institutions.
Let’s understand it with the help of an example. A bank that uses blockchain technology gets robbed. The money might still get stolen; however, it will be easier to trace the money with the help of blockchain technology, and as a result, there is a guarantee that the funds can be recovered.
- Decentralized Trust – One of the most prominent advantages of the blockchain is the way it verifies and tracks transactions. Blockchain as technology enables individuals and organizations to process transactions without the need for a third party or a central bank. As a single authority or organization is not controlling the information, the data remains secure. Moreover, it reduces or even eliminates hacking risks.
- Enhanced Security – When data gets recorded in a block, it cannot be altered in any way. Moreover, the data is being shared with all the blockchain users (nodes), which makes it difficult to shut down or hack. The blockchain network’s decentralized nature makes sure that the data is protected against hacks, and there is no central point of data failure. Moreover, the cryptographic nature of transactions also reduces the risk of fraud.
- Increased Efficiency – In the payment industry, there has always been an issue concerning human errors and double-entry systems. Blockchain eliminates both these risks as it offers a secure range of digital processes. The transactions are processed in real-time. As the process—from payment to settlement is free of any delays in the documentation, there are no duplicate entries in the ledger. Blockchain data is complete, accurate, and immutable.
Despite the promise of immutability and transparency, blockchain doesn’t guarantee that fraud will never happen. However, it does happen; one of the reasons could be the application/services layered on top of blockchain technology, which was not thoroughly tested. Moreover, as blockchains are decentralized, businesses must use a blockchain that can safely be coupled with services and infrastructure.

Author: Alessandro Civati